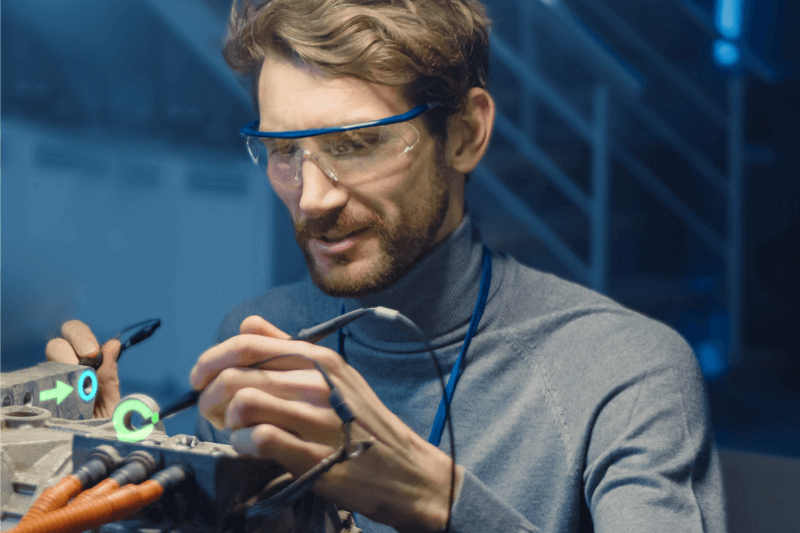

In the face of labor shortages, rising competition, and evolving customer demands, manufacturers are using connected worker technologies, like augmented reality (AR), to create a more skilled, efficient, and productive workforce.
As a manufacturing leader, your future success hinges on strategically using digital technologies to bridge the skills gap, empower your employees, and transform them into connected workers. By assessing your specific needs, investing in the right technologies, and training your employees, you can:
- Get more value from your people
- Optimize production processes
- Gain a competitive edge
Continue reading to explore the digital technologies manufacturers are using to transform their workforce into a competitive advantage and read real-world examples from companies already seeing success.
The Challenges Facing Manufacturers and Their Workforce
The manufacturing industry operates in a complex and dynamic landscape, facing numerous obstacles with far-reaching implications, including:
- Labor shortages: The manufacturing industry is facing a labor shortage, as there are not enough skilled workers to fill open positions. This is due to several factors, including the aging workforce, the decline of manufacturing in the United States, and the lack of interest in manufacturing careers among young people.
- Increased competition: Manufacturers are facing increased competition from foreign manufacturers, who often have lower labor costs. This is making it difficult for companies to compete on price and forcing them to find creative ways to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Changing customer demands: Customer demands are changing, as consumers are demanding more customized products and shorter lead times. This is putting pressure on manufacturers to be more flexible and responsive to customer needs.
- Digital transformation: Automation, additive manufacturing, and other digital transformation technologies are changing the way products are made. This is creating new opportunities for manufacturers, but it is also creating challenges, as manufacturers need to effectively implement these technologies and train their workforce to ensure adoption.
While these challenges pose significant hurdles, manufacturers that embrace digital transformation to empower their workforce are better equipped to overcome them.
Empowering the Connected Worker with Digital Augmentation

In today’s dynamic and highly competitive manufacturing landscape, creating a connected workforce is crucial to success. According to research from Kearney, 72% of factory tasks are performed by humans, and 71% of the value created by the operation comes from human actions.
However, the manufacturing industry is undergoing a digital transformation, and this is having a significant impact on the workforce. In the past, manufacturing jobs were often repetitive and low-skilled. However, as manufacturing becomes more sophisticated, jobs are becoming more complex and require a higher level of skill.
Using digital augmentation and connected worker technologies, companies can bridge the talent gap and help employees develop the skills they need to succeed in the digital age of manufacturing. By combining the best of technology with human ingenuity, companies can create a workplace of connected workers who are empowered to reach new levels of quality and productivity. In the process, companies not only improve their workforce’s skills but also make their workplaces more attractive to potential employees.
The key is choosing the right technologies for the specific needs of your workforce and your business. Here are some examples of how digital augmentation is being used to create a more connected manufacturing workforce:
1: Augmented Reality Empowers the Connected Worker with Visual Guidance
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the real world to provide employees with real-time guidance and information as they work. This can include schematics, instructions, warnings, and data about the environment. For example, a connected worker using projected AR for assembly or inspection could see work instructions superimposed directly on the product itself. AR can also be used to create personalized training programs to help employees learn new skills more quickly and efficiently. By providing real-time guidance and feedback to employees, manufacturers can improve the quality of products and reduce the risk of defects.
2: Collaborative Robots (Cobots) Provide the Connected Worker with a Helping Hand
Cobots are robots that are designed to work alongside humans in shared workspaces. They are typically smaller and less powerful than traditional industrial robots, and they are equipped with sensors and safety features to prevent collisions and injuries. They can be used to perform tasks that are hazardous or repetitive, such as welding, painting, and lifting heavy objects. This can help improve safety and productivity while freeing up human workers to focus on more complex tasks.
3: Machine Vision: The Eyes of the Connected Worker
Machine vision systems use cameras and image processing algorithms to inspect products and ensure quality standards. With the ability to detect defects or variations invisible to the human eye, machine vision helps the connected worker reduce errors and perform tasks with greater accuracy.
4: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Equip the Connected Worker with Valuable Insights
By using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to collect and analyze large datasets, the connected worker can gain valuable insights that help them make better decisions about their operations and people. For example, AI and ML can analyze data from machines to predict when equipment maintenance is needed. They can also be used for demand forecasting and supply chain optimization, helping manufacturers anticipate market trends and streamline logistics. Companies can also use AI and ML to gather workforce performance data and identify areas where workers may require additional training or support.
5: Digital Twins Give the Connected Worker the Power of Foresight
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets, such as machines, production lines, or entire factories. They are created using data from sensors and other sources to generate a precise digital representation of the real-world asset. Digital twins can be used to simulate and analyze real-world scenarios, enabling connected workers to improve product design, maintenance, and efficiency.
6: 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing Gives Connected Workers the Ability to Create On-demand
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital model. It allows for rapid prototyping and the production of complex, customized parts. This empowers designers and engineers to quickly iterate and test ideas, and to produce products that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
These digital augmentation and connected worker technologies are transforming the manufacturing industry by combining the strengths of manual and automated processes to enhance employee capabilities and improve safety, productivity, efficiency, and quality across manufacturing operations.
While manufacturers often adopt a combination of these tools to fit their needs, AR is one of the most versatile digital augmentation technologies for manufacturing. It addresses a wide spectrum of challenges and seamlessly integrates with machine vision, AI/ML, and other tools to empower workers in transformative ways. AR also bridges the gap between the digital twin and the physical world, enabling real-time communication, collaboration, and process optimization.
Augmented Reality: The Next Frontier for Workforce Transformation
Augmented reality (AR) is one of the most promising digital technologies transforming the manufacturing landscape, providing the connected worker with many competitive advantages. From training and quality control to productivity and safety, let’s explore how AR enhances workers’ experience and performance by guiding them through complex tasks for the greatest efficiency and productivity.
How AR Empowers the Connected Worker with Better Training

According to a survey by Gartner, 57% of manufacturing leaders say their organization lacks skilled workers to support digitization plans.
In today’s manufacturing landscape, where rapid adaptation to modern technologies and processes is imperative, training plays a pivotal role in preparing the workforce for success. With AR technology, connected workers can receive real-time, on-the-job training, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional training methods while also improving the effectiveness of the training.
In fact, research from the WEF (World Economic Forum) shows that businesses reported an increase in training effectiveness by up to 80% compared to traditional training regimens.
By projecting work instructions directly onto any work surface, AR helps simplify complex manual processes and makes it easier and faster to train, upskill, and cross-train employees. This reduces the ramp-up time for new and reassigned employees and empowers them to hit their productivity and quality goals from day one.
- Interactive simulations: AR training modules replicate real-world scenarios, allowing employees to gain on-the-job experience without disrupting actual production processes. For example, AR can be used to train employees on how to operate new machinery, troubleshoot problems, or perform complex tasks, and allows workers to practice these tasks in a controlled environment.
- Real-time guidance and feedback: As workers are learning a new task, AR can be used to provide trainees with instant feedback. This helps trainees identify and correct errors on the spot, accelerating the learning curve and reducing the time it takes to learn new skills.
- Personalized training: AR delivers personalized training experiences. Customized training modules can be tailored to meet specific skill development needs, whether it’s assembling a new product, mastering quality, or learning safety protocols.
- Engaging and interactive learning: AR can make training more engaging and interactive. This hands-on experience boosts engagement and retention, helping employees grasp concepts more effectively.
How AR Helps the Connected Worker Achieve Higher Levels of Productivity
AR isn’t just a game-changer for training; it’s also a pivotal tool for boosting productivity on the factory floor. By projecting visual instructions directly onto an operator’s workspace, AR can be used to streamline complex processes, standardize tasks, and eliminate non-value-added work.
- Streamline complex processes: With AR, connected workers no longer need to sift through lengthy instruction manuals or decipher complex diagrams. Instead, they receive intuitive, step-by-step guidance at their fingertips, ensuring they have the right information, when and where they need it. For example, AR can be used to provide workers with information about the location of tools and materials, guide operators through complex assemblies, or even provide real-time feedback on the alignment of a part or tightness of a screw. This eliminates the need for technicians to recall instructions from memory and can help reduce the risk of missed steps. As a result, workers are empowered to make informed decisions quickly and can complete tasks more efficiently.
- Eliminate non-value-added work: By providing workers with information about the most efficient way to complete tasks, they can follow optimized procedures that maximize efficiency and minimize unnecessary steps. As a result, connected workers execute tasks with greater speed and accuracy, resulting in shorter production cycles and faster time to market.
- Standardize processes for improved quality: This standardized approach also ensures products are built the same way across shifts and plant locations, resulting in shorter production cycles, faster time-to-market, and a workforce capable of meeting customer demands with agility and precision.
How AR Helps the Connected Worker with Quality Control
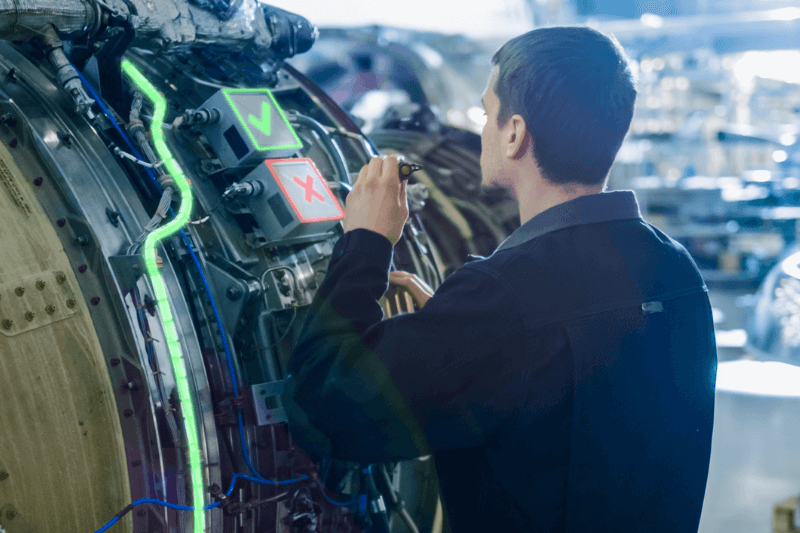

In an industry where people perform most factory tasks, and 80% of defects are caused by human errors, manufacturers need a proven way to eliminate variability and ensure workers get the job done right – every time. AR enables the connected worker to produce products faster and more efficiently while ensuring that products are assembled correctly and meet quality standards.
One of the primary ways AR enhances manufacturing quality is through real-time error prevention and defect detection. AR’s standardized workflows ensure that each worker completes tasks in a consistent and precise manner. By projecting visual instructions directly onto the operator’s workspace, AR minimizes variations in processes and reduces the likelihood of human error. This guarantees that every step is carried out consistently, resulting in products that adhere to quality standards.
AR systems can also be equipped with 3D sensors and vision cameras that detect deviations and anomalies as tasks are performed. This allows for instant identification of potential issues, reducing the risk of defects. By catching problems early, manufacturers can take swift corrective action, minimizing costly rework and improving overall product quality.
In the process, AR enables manufacturers to capture real-time operational data for full traceability into manual manufacturing processes. This data-driven approach empowers manufacturers to identify areas for process optimization and improve their overall efficiency and productivity.
How AR Improves Human Factors, Workplace Ergonomics & Safety
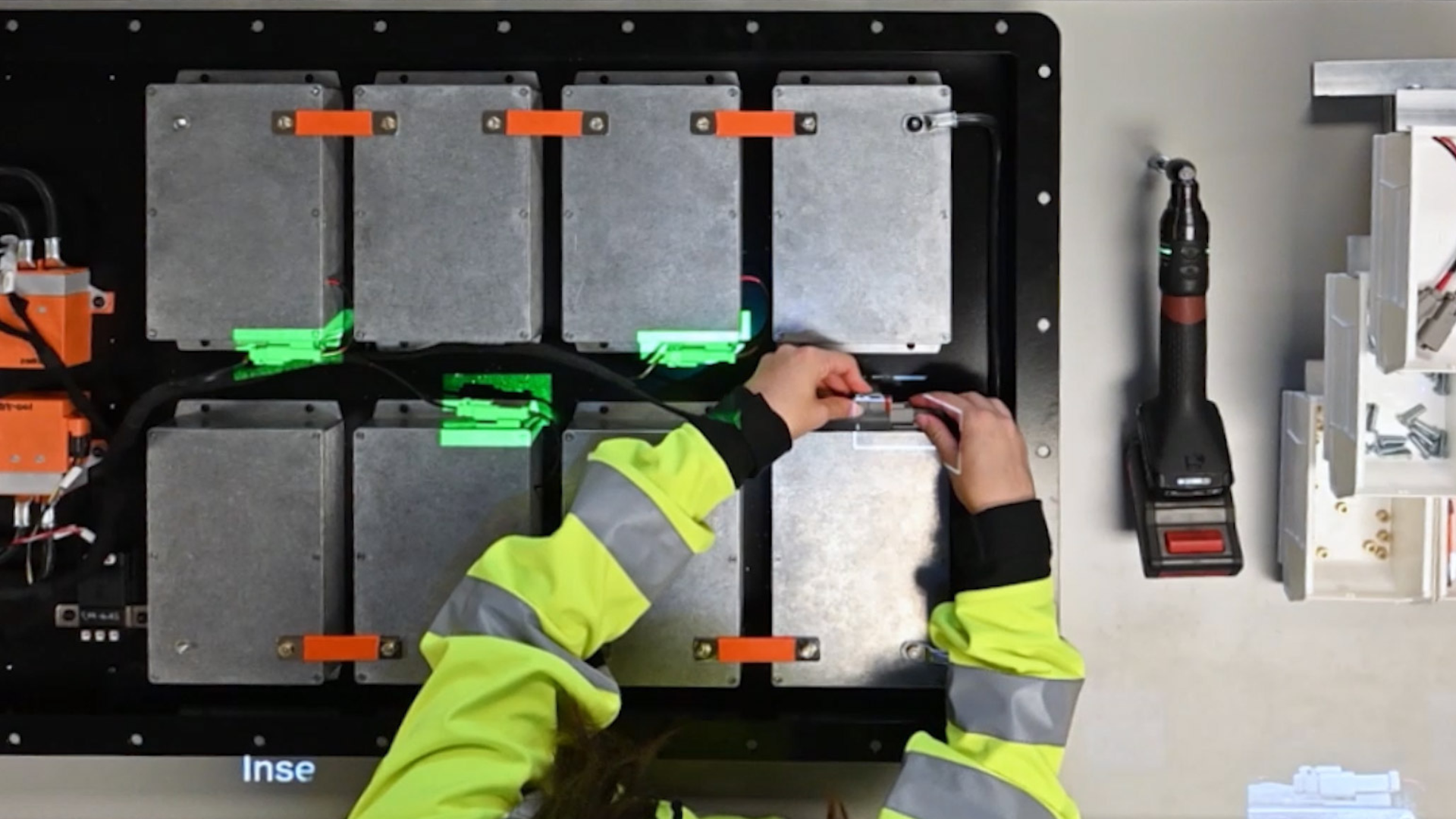

Ergonomics and human factors engineering are both concerned with designing systems and workplaces that are safe, efficient, and comfortable for humans to use. AR has the potential to revolutionize ergonomics and human factors engineering in manufacturing by enabling workers to interact with their environment, tools, and tasks in new and innovative ways, resulting in safer, more efficient, and more productive workplaces.
AR’s ability to provide real-time information, guidance, and feedback directly within a worker’s field of view aligns with the principles of ergonomics and human factors engineering by making complex tasks more intuitive and less physically and cognitively demanding. This not only reduces the risk of human error but also contributes to a safer and more productive work environment.
For example, AR can help workers maintain proper posture and avoid repetitive strain injuries by projecting instructions onto their field of vision. This eliminates the need for them to look down or away at a screen or manual, which can reduce fatigue and discomfort.
With AR, connected workers are also at reduced risk of mishandling components that could lead to safety hazards. This is especially important in hazardous environments, such as those involving heavy machinery or chemicals. In these instances, AR can be used to provide employees with instructions on how to safely operate machinery or how to identify and avoid hazardous materials. By providing real-time instructions and warnings to employees, companies can ensure workers follow inspection and safety guidelines to prevent accidents and injuries.
Learn more about the role of AR in the ergonomic workplace of the future.
How AR is Empowering the Connected Worker in the Age of Automation
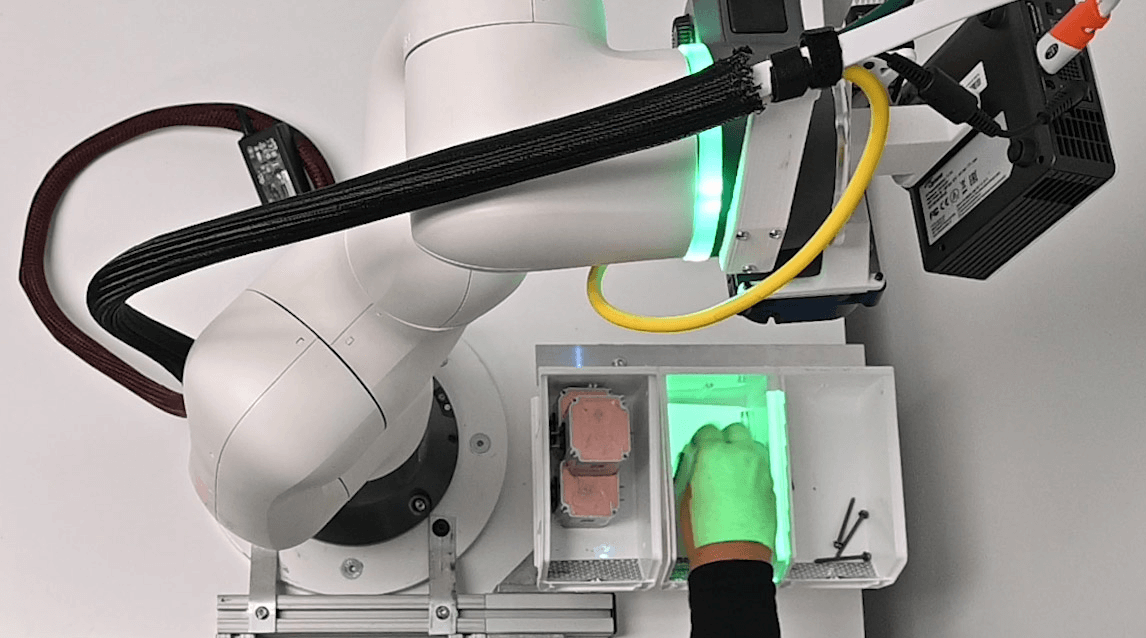
As humans and robots increasingly collaborate in manufacturing, workers need the knowledge to manage and maintain automated systems. AR empowers the connected worker with real-time guidance, enabling them to do this effectively and efficiently.
For example, AR can be used to:
- Improve the maintainability of robots and other automated systems: AR can be used to provide maintenance technicians with real-time visual guidance on how to repair or maintain robots and other automated systems. For example, AR can be used to highlight the location of a faulty part in a robot or to guide a technician through replacing a part in a machine. This helps workers troubleshoot problems with robots and automated systems more quickly and efficiently, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
- Maximize the collaboration between humans and smart systems: The future of manufacturing is about people and machines working together to co-create a new way of working, where machines do what machines do best—fast repetitive processes, and people do what people do best—think, solve, and create. This is where AR can seamlessly blend innovative technology with human ability to help workers harness the power of augmented intelligence and cobots to maximize performance.
Empowering a Diverse Workforce and Solving Labor Shortages with AR

As the manufacturing workforce ages and retires, filling roles with new hires is becoming increasingly difficult. According to a study by Deloitte and The Manufacturing Institute, the manufacturing skills gap in the U.S. could result in 2.1 million unfilled jobs by 2030. The cost of those missing jobs could potentially total $1 trillion in 2030 alone.
The use of inclusive and assistive manufacturing technologies, like AR, can help businesses solve these labor shortages. By making it easier for individuals with differing abilities to participate in the workforce, AR can help businesses tap into a new pool of potential employees.
According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 1.3 billion people (16% of the world’s population) experience significant disability. AR can empower a diverse workforce by providing individuals with differing abilities the tools and resources they need to perform their jobs safely and efficiently. This can help reduce barriers to employment and create a more inclusive workplace.
For example, AR can be used to:
- Provide visual instructions and feedback to workers who speak a different language or are deaf or hard of hearing.
- Magnify objects or other visual aids to workers who have impaired vision.
- Simulate training environments that allow workers with disabilities to learn new tasks and practice skills without risk of injury.
The benefits of an empowered and diverse workforce are numerous. A diverse workforce brings a wider range of perspectives and experiences to the table, which can lead to better decision-making and more innovative solutions. In addition, a diverse workforce is more likely to reflect the customer base, which can help businesses to better understand and meet the needs of their customers.
Real-world Examples of Connected Workers Using AR in Manufacturing
Numerous case studies prove the benefits of AR for manufacturing. Let’s explore several examples from different industries to see how AR can transform manufacturing by empowering the connected worker.
Automotive Manufacturer Adopts AR Work Instructions for Error-free EV Assembly
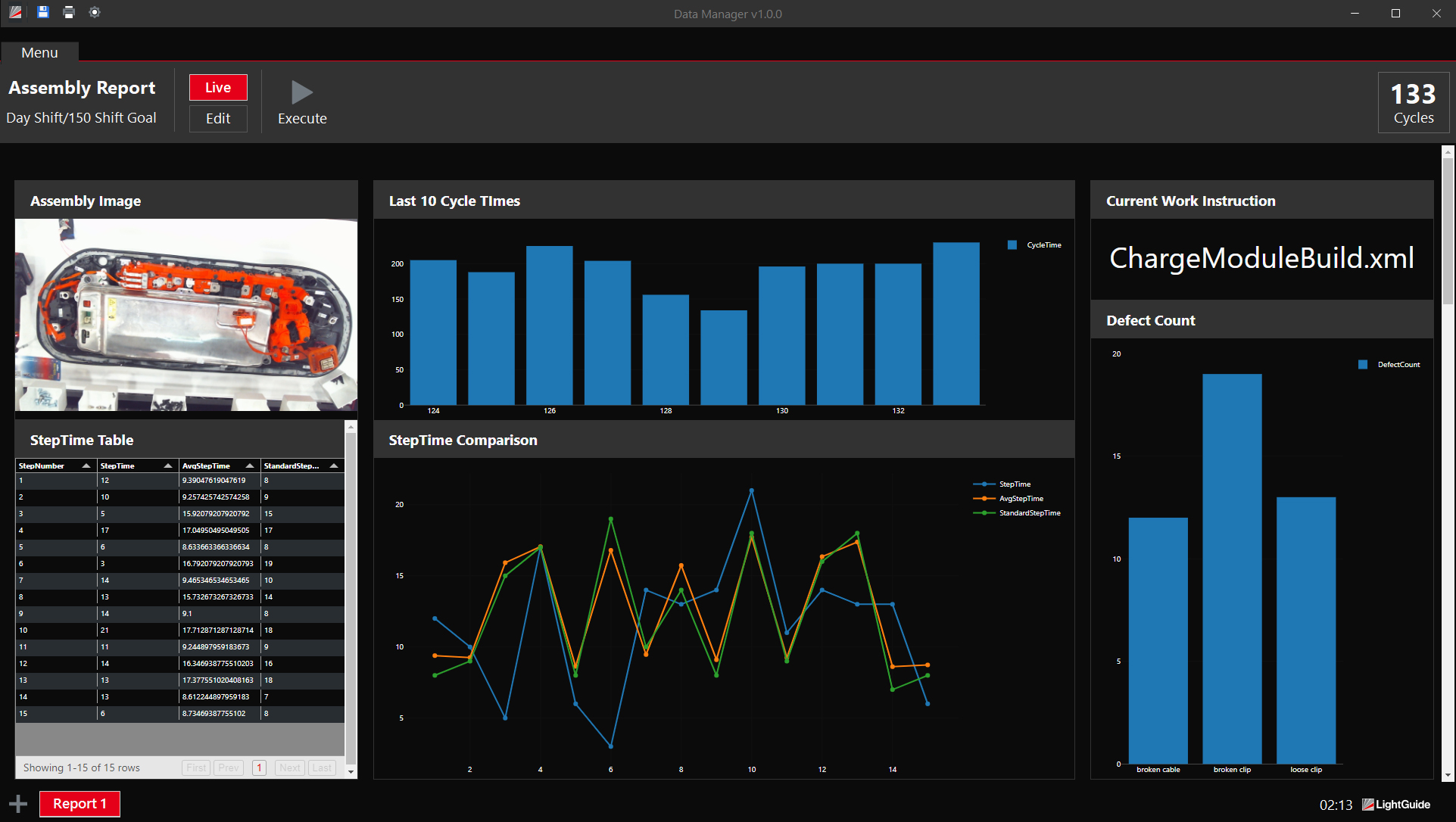
Lightning eMotors uses AR to assemble battery-electric vans, trucks, and buses. Using LightGuide’s projected AR work instructions to standardize and streamline assembly workflows, the company has been able to improve quality, efficiency, and safety. AR instructions guide connected workers through complex assembly tasks in real time, ending the need to memorize procedures and reducing errors. This has resulted in a 50% decrease in cycle time and a 75% decrease in training time.
AR has also helped Lightning eMotors bridge the experience gap in its workforce, empowering operators with diverse backgrounds to perform at their best. By simplifying complex processes and providing comprehensive guidance, AR has increased worker focus and confidence, reduced stress levels, and made work more enjoyable. This has led to improved productivity, accuracy, and safety. Additionally, AR has enabled Lightning eMotors to accelerate the deployment of work instructions and improve the effectiveness of its training programs.
Leading Aerospace Manufacturer Eliminates Defects with AR Technology
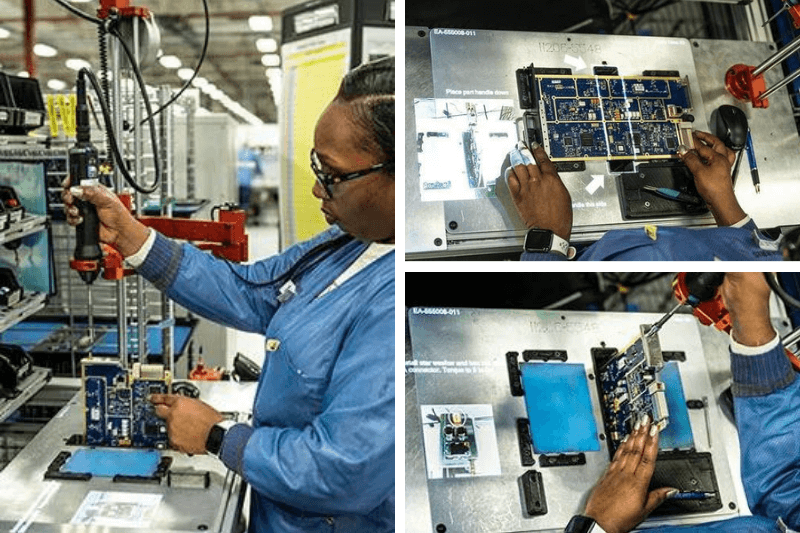
L3Harris Technologies, an aerospace and defense manufacturer, implemented LightGuide’s AR software to standardize work instructions and reduce the cognitive load on workers. The system also uses infrared and 3D sensing to track the operator’s hand position and provide real-time feedback on their progress.
As a result of implementing LightGuide, L3Harris has been able to eliminate assembly-related defects and make better, data-driven decisions. The company has also been able to streamline its processes and reduce the cognitive load on its workers. For example, on a line with 17 variants of one product, LightGuide helped to consolidate parts and eliminate changeover per variant. This resulted in zero assembly-related defects. Overall, LightGuide has helped L3Harris improve the quality of its products, increase efficiency, and reduce costs.
Empowering Workers with Disabilities AR Case Study
Mariasteen is a Belgian manufacturing company that employs over 700 people with disabilities as their manufacturing operators. They use two technologies to increase accessibility for these workers: LightGuide and cobots.
LightGuide’s projected AR platform provides workers with step-by-step digital instructions for assembling products. This has helped improve throughput by 50% and reduce quality defects to almost zero. LightGuide has also had a positive impact on the operator’s experience, making workers feel more empowered and less stressed.
Another benefit of LightGuide is that it lowers the language barrier to employment. The system overlays icons, designs, and animations to communicate instructions, rather than relying on written text. This makes it easier for people with cognitive disabilities to understand and follow instructions.
Overall, Mariasteen is a fitting example of how technology can be used to improve the lives of people with disabilities and enable them to participate more fully in the workforce.
These case studies demonstrate that AR is not just a theoretical concept, but a proven and successful solution. Leading companies like L3Harris, Lightning eMotors, and others have already embraced AR to elevate their performance, productivity, and efficiency. Their achievements serve as a testament to the transformative potential of AR, offering inspiration for others to follow suit.
Explore additional case studies of AR used in manufacturing across industries
Transform Your Workforce into a Competitive Advantage with Digital Augmentation
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, it’s clear that digital augmentation will continue to play an increasingly significant role in transforming the future of work. Factories of the future will use digital augmentation to bridge the skills gap and enhance human capabilities by equipping workers with the tools they need to excel in more complex tasks, making manufacturing jobs safer and more efficient. Companies that fail to adapt their manufacturing processes risk being left behind by competitors who are focused on improving productivity through better use of talent and equipment.
By adopting assistive technologies, companies can empower workers to be more effective in their roles and get the best from automated and human performance. AR is a key technology fostering this transition and offers a wealth of benefits that enable manufacturers to leverage their greatest asset: people.
AR revolutionizes the manufacturing industry in four key ways:
- Training: AR immerses employees in interactive modules to enhance their skills in a safe and realistic environment.
- Safety: AR provides real-time instructions and warnings to safeguard employees from potential accidents.
- Productivity: AR delivers crucial information directly to workers, streamlines workflows, and maximizes output.
- Quality control: AR empowers workers with real-time data, leading to higher-quality products and improved customer satisfaction.
As you embark on this new era of manufacturing, remember that the journey is a continuous one. The landscape of technology will continue to evolve, and so should your strategies. By embracing digital augmentation, you can bridge the skills gap and empower your workforce to achieve greater levels of success in the workplace while securing your position as a leader in the dynamic world of modern manufacturing.

Ready to Explore How AR Can Give Your Workforce a Competitive Advantage?
Connect with our team to see how the LightGuide platform can transform your operations.





