Trusted by the World’s Leading Electronics Companies
 |
 |
 |
 |
Resolve Common Electronics Manufacturing Challenges with AR Work Instructions
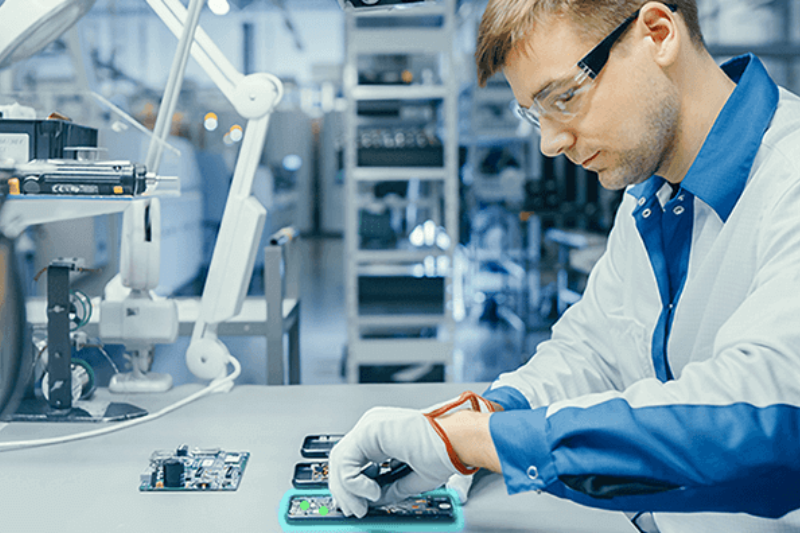
In an industry grappling with constant innovation, short product lifecycles, and high variation, where human errors account for many defects, electronics companies are rethinking how they approach assembly, repair, and recycling to achieve higher levels of quality and productivity.
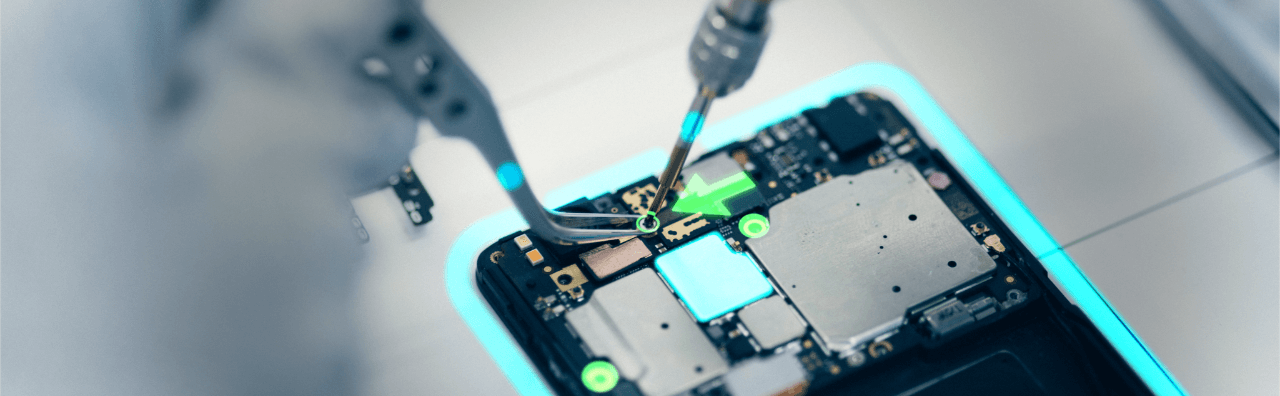
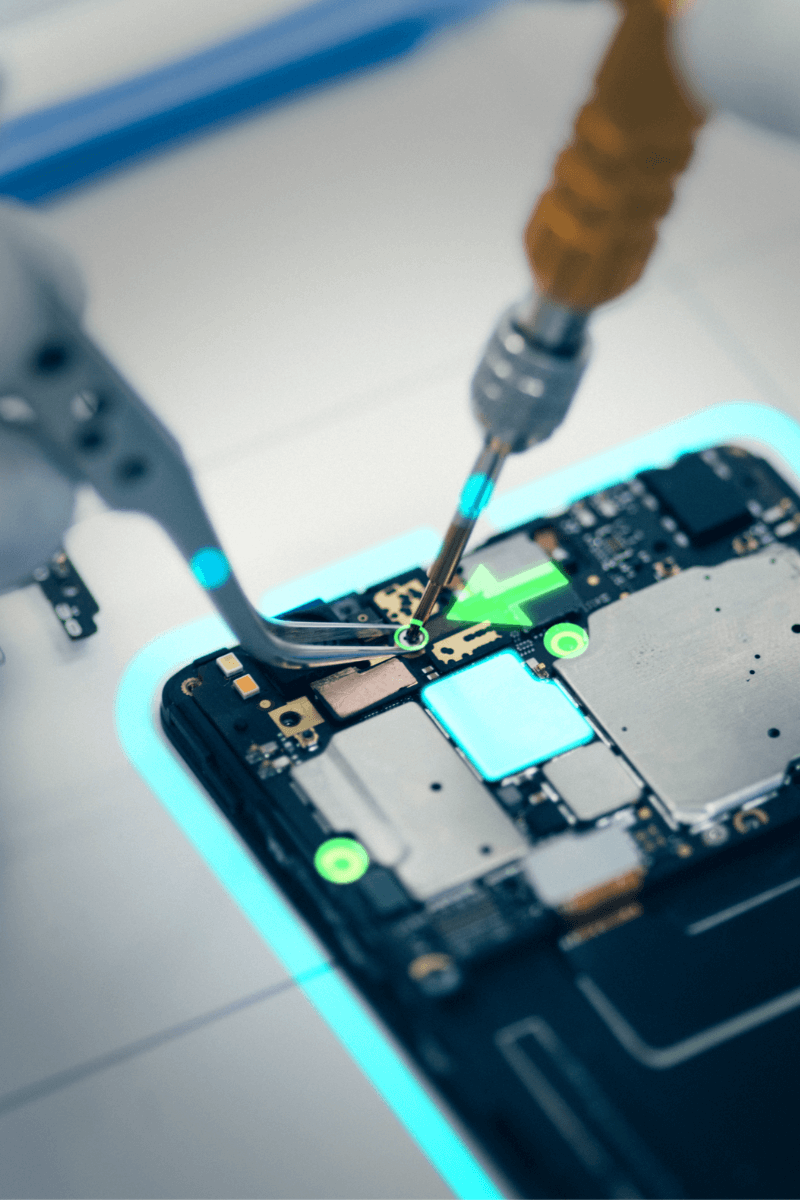
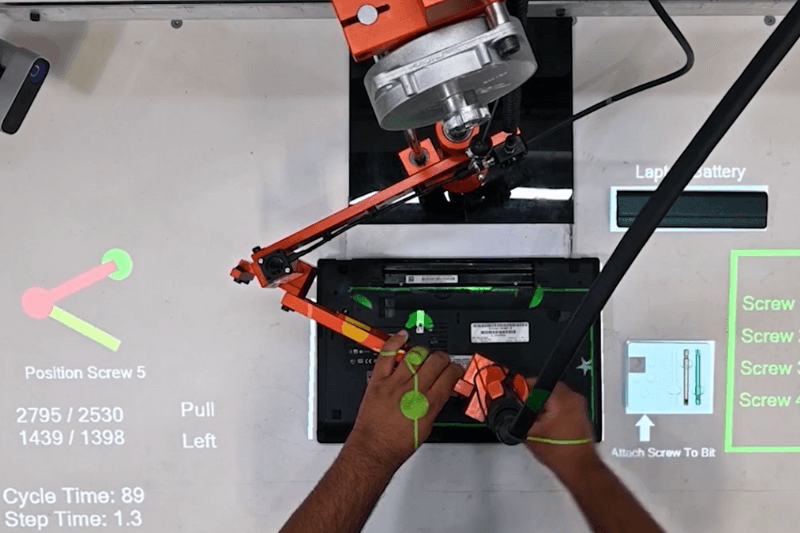
LightGuide’s projected augmented reality (AR) work instructions drive standardization, efficiency, and quality by providing operators with precise, real-time guidance for complex manual processes.
Unlock the Power of AR Workflows with LightGuide
As the premier digital work instruction platform, LightGuide’s projected AR software interfaces with industrial-grade projectors, sensors, and smart tools to guide technicians through each step of the process.
- Standardize manual processes and reduce complexity by transforming instructions into visual workflows that guide technicians in real-time
- Prevent errors with integrated sensors and vision cameras that confirm tasks are completed correctly
- Improve traceability and gain insight into valuable data, with the ability to track cycle time, throughput, defect rates, and more
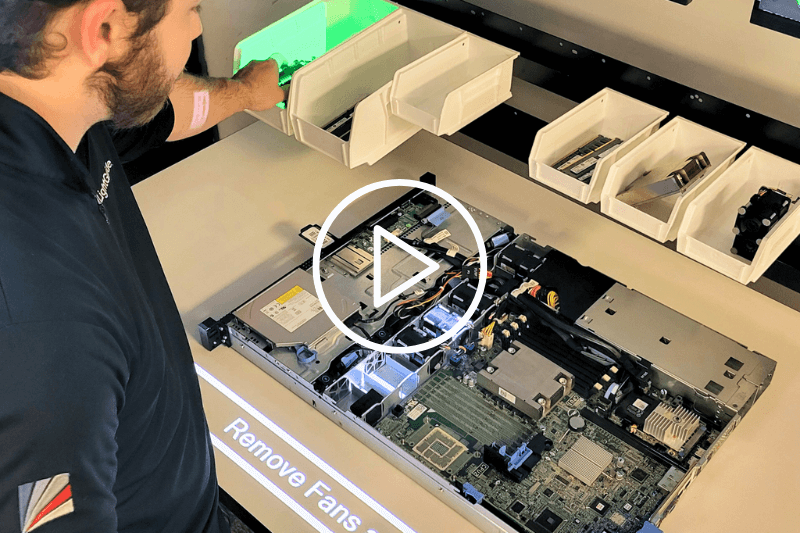
Video
LightGuide AR Delivers Proven Results
- 90%+ Quality Improvement
- 70%+ Training Efficiency
- 50%+ Productivity Increase

Your Guide to AR Applications on the Factory Floor
Not all types of augmented reality are created equal. Use this guide to discover which type of industrial AR is best suited for your factory application, learn from real-world case studies, and more.
|
 |
Leading Manufacturers Have Dramatically Improved Their Processes. So Can You.
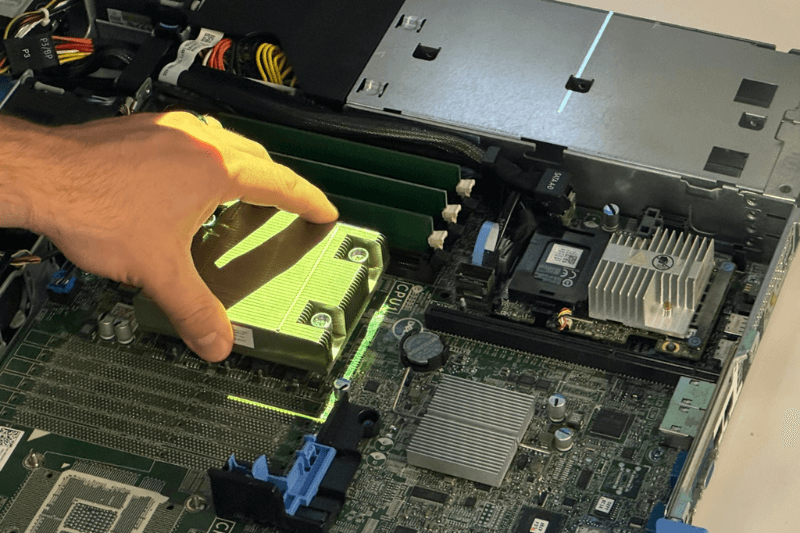
Scale Data Center Infrastructure and Hardware Manufacturing with AR
As demand for data center infrastructure surges, manufacturers are using AR work instructions to scale production of servers, cooling systems, power distribution units, and networking hardware.
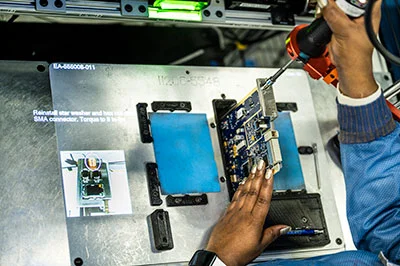
Tech Company Transforms Electronics Repair Processes with AR
Using projected AR, this company reduced complexity and standardized repair processes by digitizing workflows and providing technicians with precise visual guidance.
Aerospace & Defense Electronics Manufacturer Eliminates Defects
After implementing LightGuide AR work instructions on a line with 17 variants, L3Harris eliminated defects and changeover per variant.
Using Projected AR for Rack Server Refurbishment
See how LightGuide’s projected AR work instructions guide technicians through server refurbishment with real-time, step-by-step instructions projected directly onto the device.
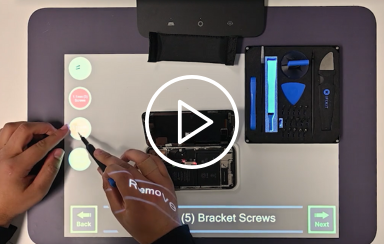
Streamline Electronics Repair with Projected AR
With projected AR, repair processes can be standardized to reduce complexity, optimize efficiency, and eliminate errors, enabling technicians to achieve consistent, repeatable outcomes when working on different devices.
5 Electronics Manufacturing Challenges Augmented Reality Solves
From severs and smartphones to circuit boards and 5G wireless transmitters, here are five ways augmented reality streamlines and error-proofs electronics assembly, maintenance, and repair.
Testimonials
"[LightGuide] puts work instructions exactly where you build your product, so you’re reducing time looking at printed instructions by putting the focus exactly where operators’ attention should be."
Let Us Design a Solution for Your Most Challenging Application
Ready to put the power of projected AR to work for you? Our proven platform, deployed across 200+ customers, can deliver predictable results for your most complex manual processes.